Transformers in Hugging Face
2022/11/23 19:30:00
2022/11/25 22:30:00
note
hugging face
transformers
Hugging Face 的入门教程,目标是从0开始训练自己的大模型。
重点教程
- 组装所有的组件:https://huggingface.co/course/chapter2/6?fw=pt
- processing data: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter3/2?fw=pt
- Fine-tune: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter3/3?fw=pt
- Full training: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter3/4?fw=pt
- Train a new tokenizer from a old one: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter6/2?fw=pt
- Use open source dataset: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter5/1?fw=pt
- Check tokenizers is fast or not: https://huggingface.co/course/chapter6/3?fw=pt
- Normalization and pre-tokenization (maybe we won’t use): https://huggingface.co/course/chapter6/4?fw=pt
1. Hugging Face
pipeline: 一个端到端的transformer实现,可以直接用于接收文本信息,得到模型在下游任务上的向量表示,并最终处理为人类可理解的形式。
pipeline = tokenizer + model + post processing
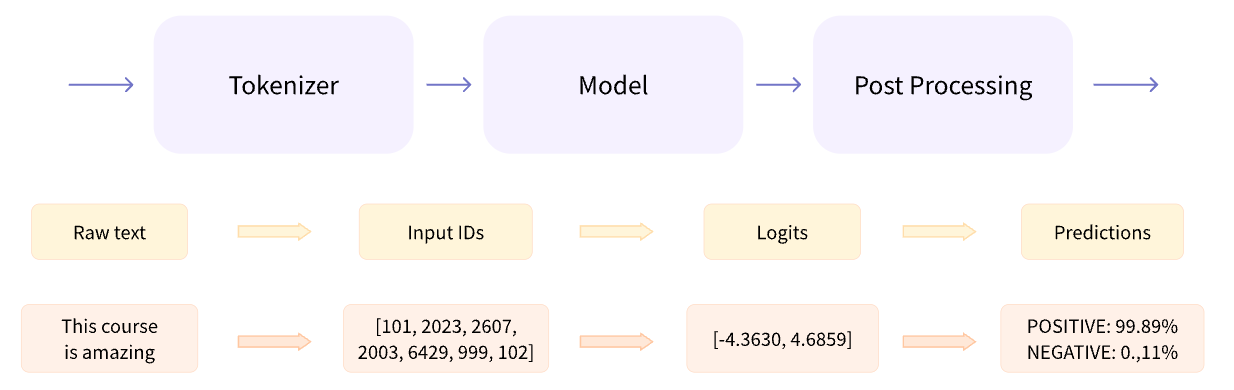
1.1 Tokenizer
tokenizer:
- [分词] Splitting the input into words, subwords, or symbols (like punctuation) that are called tokens
- split on spaces
- Character-based
- sub-word tokenization
- [查表] Mapping each token to an integer
- [add attention mask, etc] Adding additional inputs that may be useful to the model
# load a pretrained tokenizer
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
# get result
raw_inputs = [
"I've been waiting for a HuggingFace course my whole life.",
"I hate this so much!",
]
inputs = tokenizer(raw_inputs, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
print(inputs)
'''
{
'input_ids': tensor([
[ 101, 1045, 1005, 2310, 2042, 3403, 2005, 1037, 17662, 12172, 2607, 2026, 2878, 2166, 1012, 102],
[ 101, 1045, 5223, 2023, 2061, 2172, 999, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]), 分词之后,每个词在词表中的id,注意这里用了word and subword分词方法,即分割词语到不可分割的常见词语为止,其中包含了用于将序列填充为等长序列的占位符
'attention_mask': tensor([
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]),have the same shape as input ids,
}
'''API:
# load
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
# use
tokenizer("Using a Transformer network is simple")
'''
{'input_ids': [101, 7993, 170, 11303, 1200, 2443, 1110, 3014, 102],
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
'''
# split (tokenize)
sequence = "Using a Transformer network is simple"
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(sequence)
print(tokens)
'''output: ['Using', 'a', 'transform', '##er', 'network', 'is', 'simple']'''
# From tokens to input IDs
ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
print(ids)
'''output: [7993, 170, 11303, 1200, 2443, 1110, 3014]'''
# decoding
decoded_string = tokenizer.decode([7993, 170, 11303, 1200, 2443, 1110, 3014])
print(decoded_string)
'''output: 'Using a Transformer network is simple''''
# save
tokenizer.save_pretrained("directory_on_my_computer")
1.2 Model
Model = transformer + model heads
transformer: input: tokenized raw data; output: high-dimensional output shape like [b, t, d]
# load pretrained transformer
from transformers import AutoModel
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
outputs = model(**inputs) # tokenized input
print(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape)
# output: torch.Size([2, 16, 768]), [b, t, d]model heads: input: output of transformer; output: the result of downstream task, maybe the output of a sigmoid network.
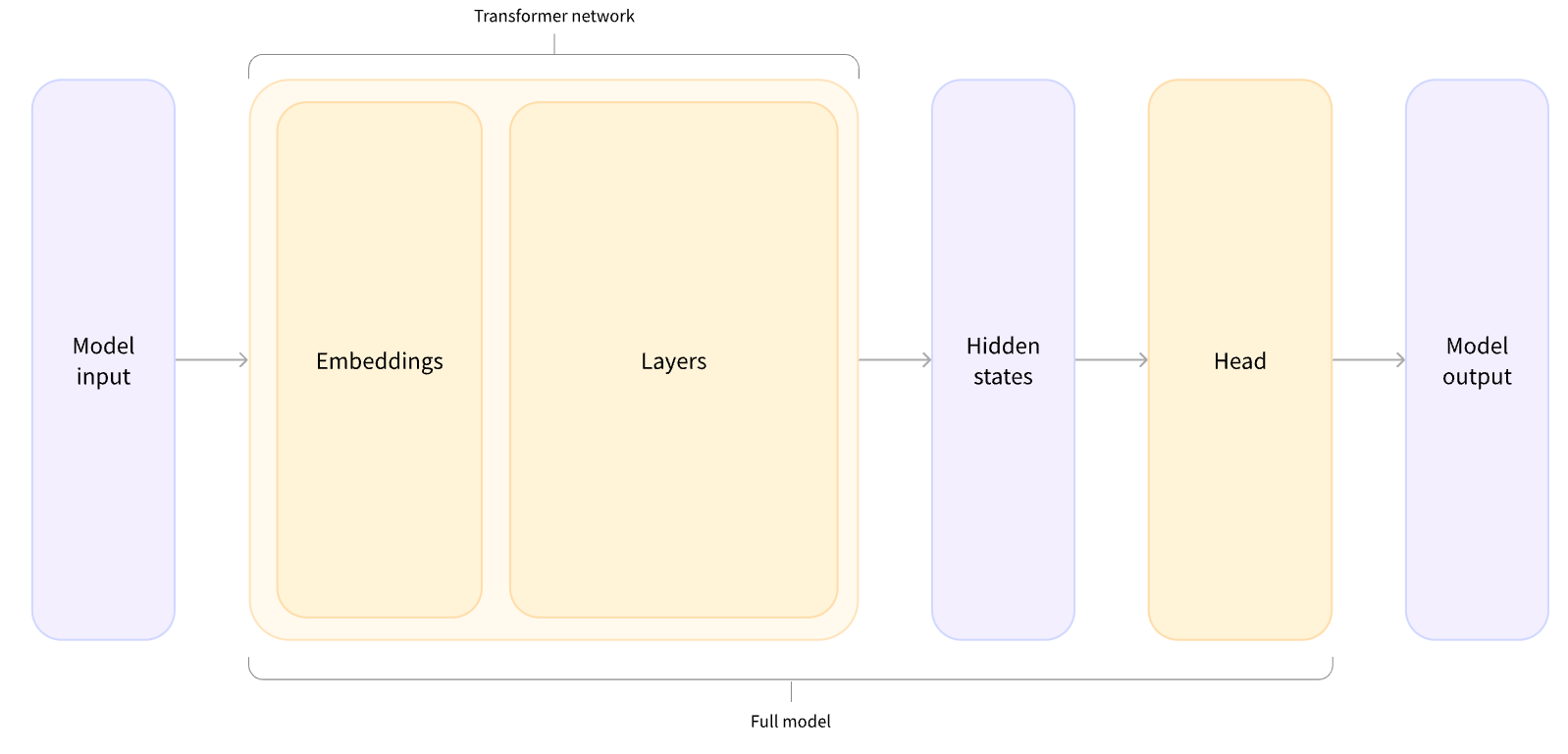
# transformer with subsequent network
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
outputs = model(**inputs)
print(outputs.logits.shape)
# output: torch.Size([2, 2]), we have just two sentences and two labels, the result we get from our model is of shape 2 x 2.The Choice of Model
*Model(retrieve the hidden states)*ForCausalLM*ForMaskedLM*ForMultipleChoice*ForQuestionAnswering*ForSequenceClassification*ForTokenClassification- and others (non-exhaustive list)
1.3 Post-processing
Map tensor value output by model head (mentioned above) to text (according to id2text, etc.).